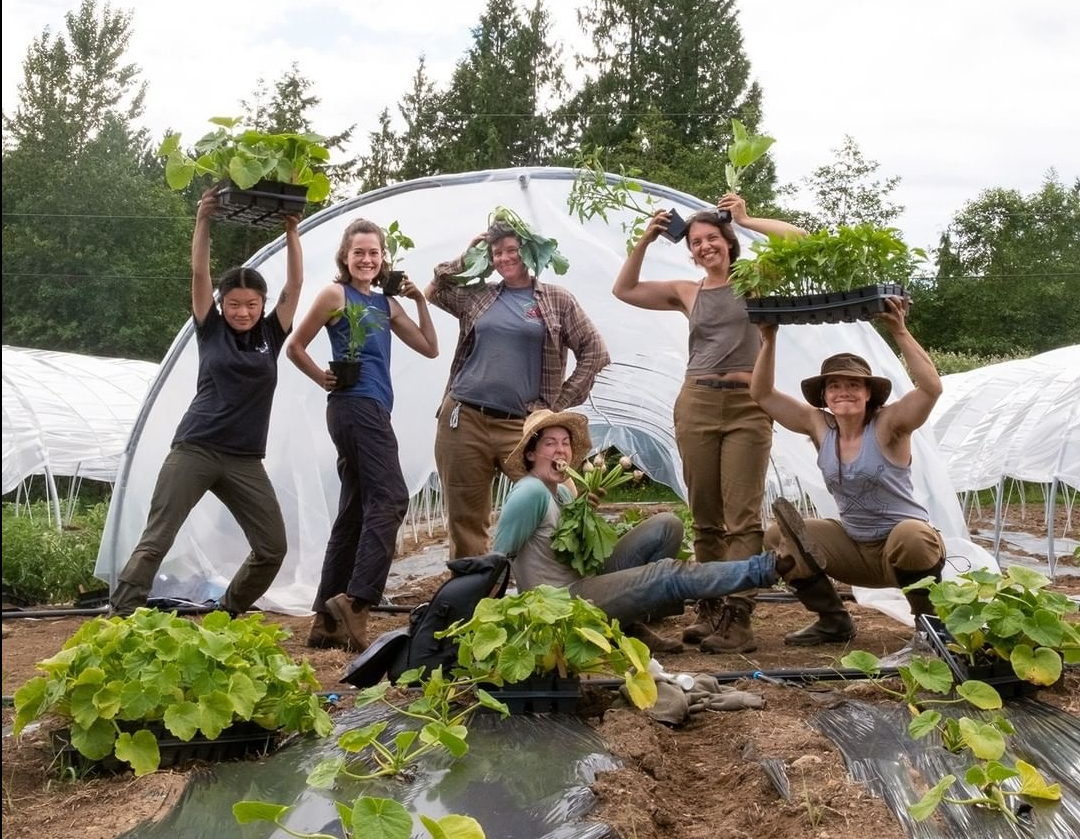
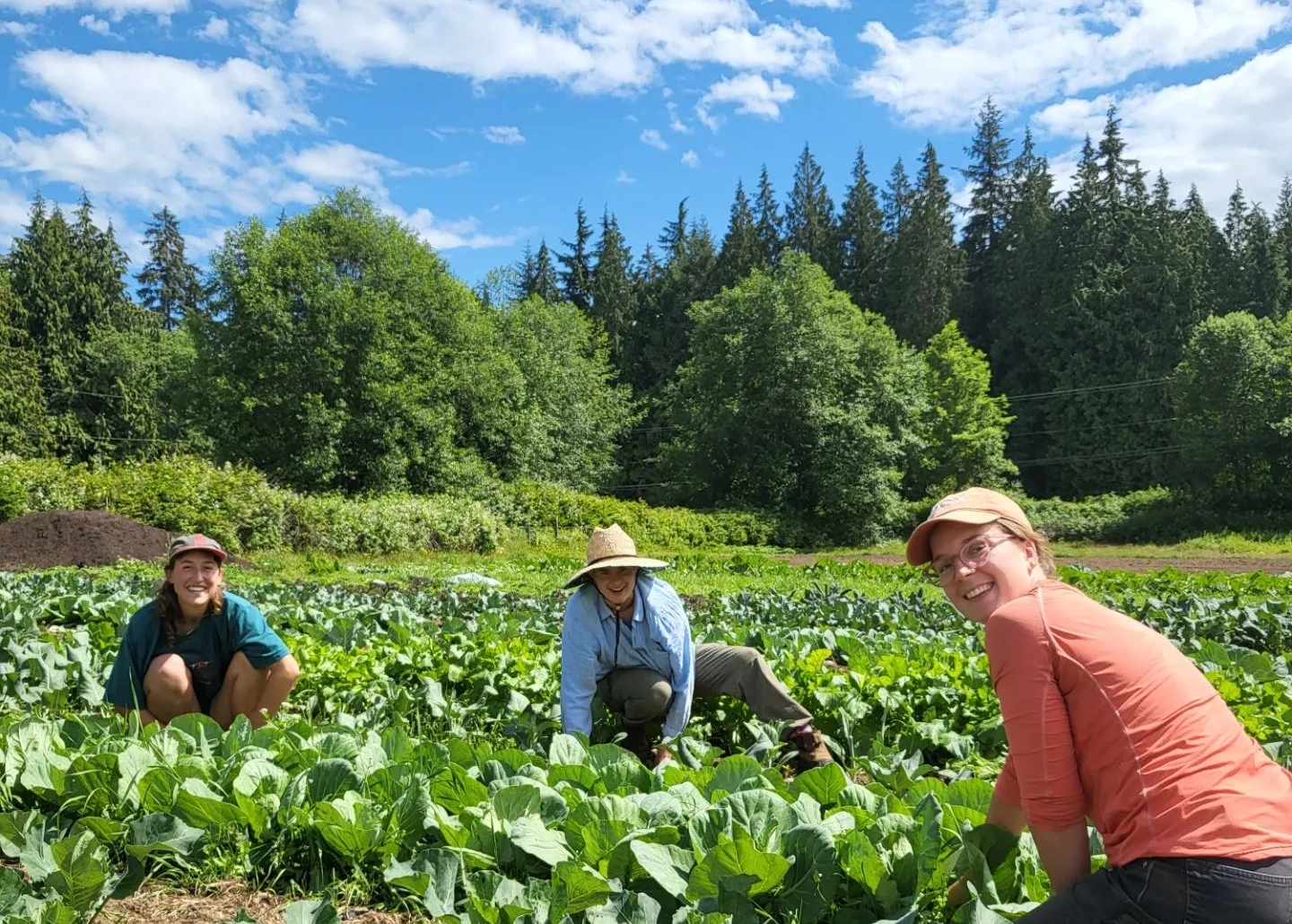
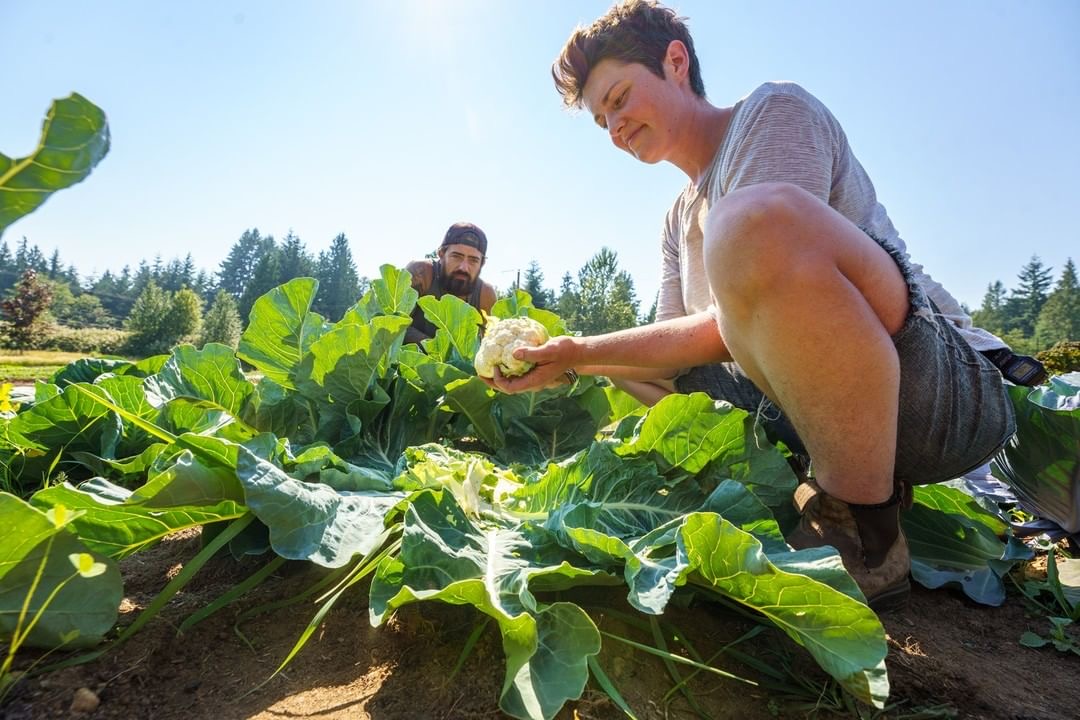
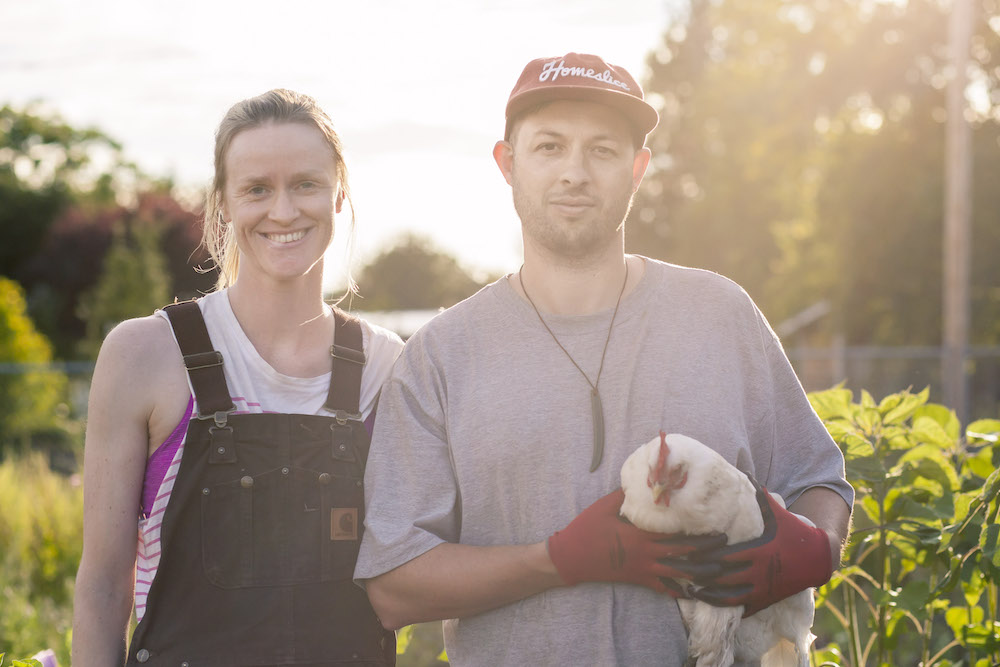
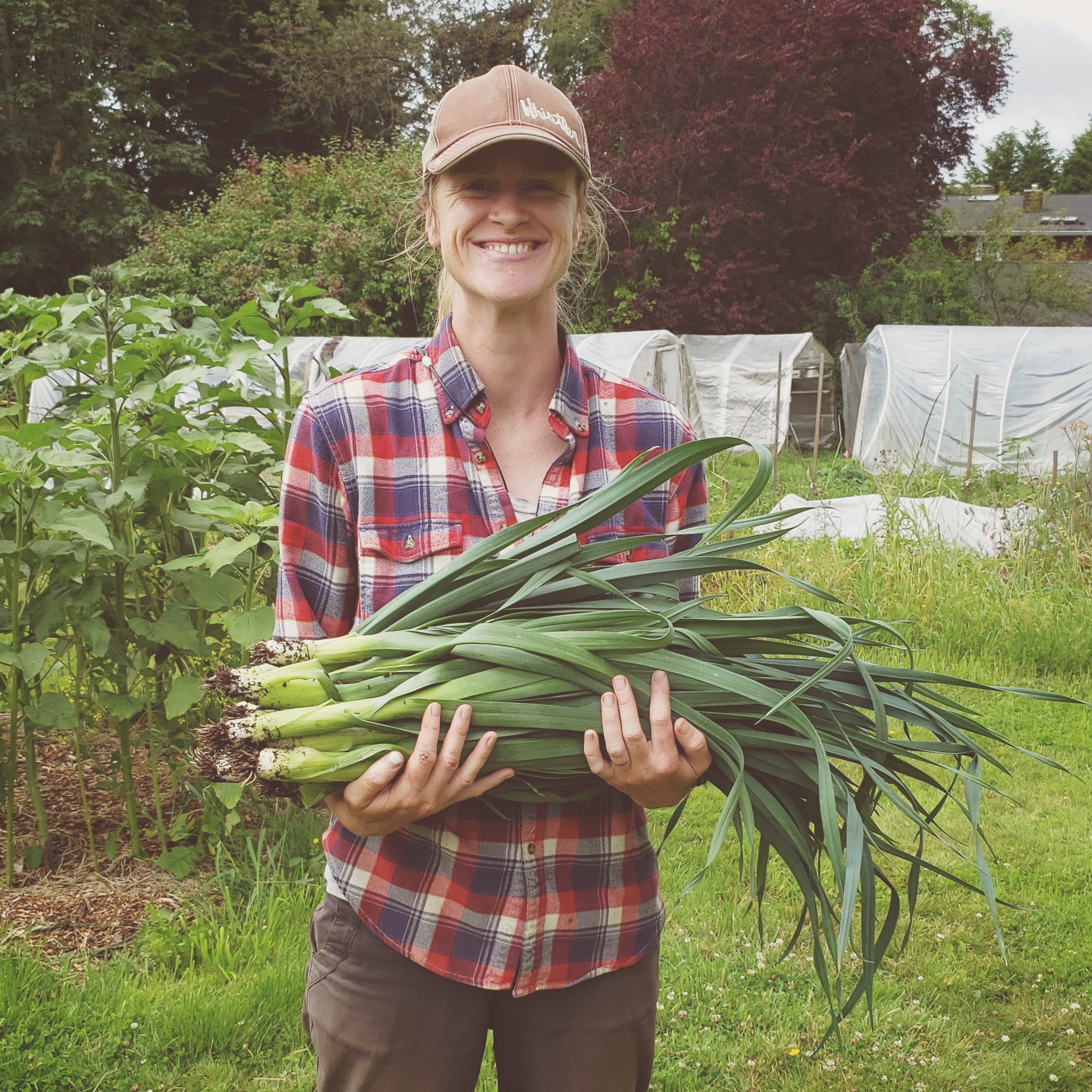
Organic Stories: Northbrook Farm, WSANEC Territory

Neither Bored Nor Lonely
Collaboration & Community
By Moss Dance
On a sunny day in light spring, I called up Heather Stretch at Northbrook Farm for a chat. The sun was shining in WSÁNEC territory on the Saanich Peninsula, and I could hear that she was busy working on something in the background while we dove into her story of farming, collaboration, community, and the organic movement.
Heather Stretch is a well-known figure in the organic world—she recently served on the Organic BC board as president, building on her 23-year history of collaborative farming. Northbrook Farm is one of the three farms that make up Saanich Organics, along with Three Oaks Farm (Rachel Fisher), just down the road in Saanichton, and Sea Bluff Farm (Robin Tunnicliffe), a little further afield in Metchosin.
The trio of farmers who began Saanich Organics (Heather Stretch, Rachel Fisher, and Robin Tunnicliffe) have been active in the organic community for many years. They also wrote a book called All the Dirt: Reflections on Organic Farming, which is part memoir, part practical guide for beginning farmers.
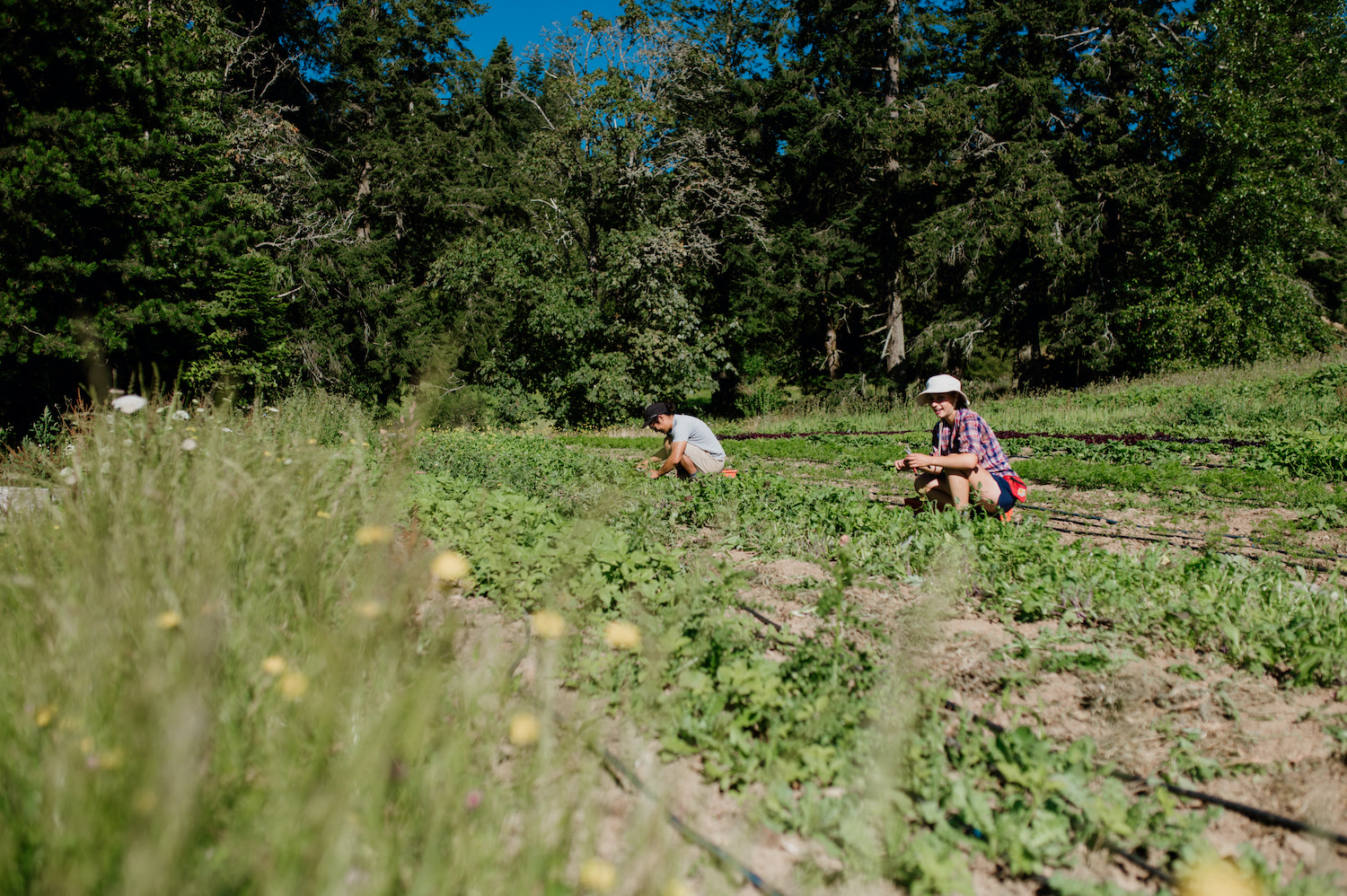

The spirit of cooperation that infuses Heather’s work is in full bloom at Northbrook Farm. The total size of the property is 20 acres—Heather and her spouse Lamont co-own the land with Heather’s aunt and uncle, Brian and Jane Stretch. On the land, buzzing like a hive of productive bees, businesses and farming friends flourish. Northbrook Farm comprises seven acres of the property, and the land is shared with Square Root Farm, an organic vegetable operation run by Chrystal Bryson and Ilya Amhrein. Rebecca’s Garden, run by Rebecca Jehn, also has a large plot to grow some warmer climate seed crops at Northbrook Farm. Brian and Jane Stretch have a plot where they grew cut flowers for many years—they now lease this area to Mayan Vered, of Flowerface Farm. Finally, Saanich Organics has a shared plot on the land, including a large greenhouse, affectionately named Long John, or LJ for short.
Of all of the agreements she has with farmers on the land, the lease arrangement with Rebecca’s Garden is Heather’s favourite: “no money changes hands at all,” she says. “Once a year, Rebecca brings me some preserves, and if it’s been a good seed year, she’ll bring me some seed, and we always have an amazing feast.”
With all of this activity, and all of these people on the land, I asked Heather what day-to-day life is like on the farm. Heather says she’s “neither bored, nor lonely.”
The Roots of Northbrook Farm
It wasn’t until Heather was in her early twenties with a freshly-minted English degree that she realized farming would be a great career for her. “Most people would assume that someone who starts an organic farm had a pre-existing passion for growing. In my case, that came later.” Heather writes in All the Dirt: Reflections on Organic Farming. “My uncle offered me land to farm, and until that moment, I had never considered farming. From the moment he mentioned it, though, it seemed like a perfect fit for me.”

The promise of working outdoors, growing food, an environmentally sustainable career, and the ability to include family in her work life convinced Heather to accept her Uncle Brian’s offer. When she met her husband Lamont, she says, “the poor guy fell in love with a woman who already had a plan.” Luckily, Lamont decided to move from North Carolina to the Saanich Peninsula with Heather to pursue her dream of farming.
“I had the great good fortune to have free land to farm for my first three years,” writes Heather. “Lamont and I decided to buy my grandmother’s portion of the land that we now share with my aunt and uncle. Fortunately, she gave us a great deal, because otherwise we probably wouldn’t have been able to afford to buy land in this area.”
Northbrook Farm’s name is a nod to Lamont’s lineage. Northbrook is a region of rural North Carolina where his father was born, and it also suits the sunny parcel of land with a brook running through it.
Trust Equals Success
Saanich Organics was founded by Heather, Robin, and Rachel’s farmer mentors, Tina Baynes and Rebecca Jehn. Heather, Robin, and Rachel purchased the business from their mentors in the early 2000s.
Sales are conducted through a CSA program, restaurants, and grocery stores. Saanich Organics’ marketing strategy has evolved with the growth of everyone’s life situations and land base. For example, Heather says, Robin moved out to Sea Bluff Farm about 10 years ago—a huge size upgrade from her original one-acre plot. “There were some adjustments there to figure out how to increase sales,” says Heather, “and we had to figure out how the business would work when the contributing farms were at very different scales.” Navigating big changes in a collectively-owned business isn’t easy, and Heather points to trust, friendship, and communication as important factors in managing growth and transition.

The Saanich Organics team have come up with a creative solution to account for the different scale of production at each of their member farms. Sea Bluff Farm has a very popular farm stand in Metchosin, so Robin also has the ability to market extra produce on her own. Rachel and Heather attend the Moss Street and James Bay Markets in Victoria. This helps to evenly distribute the marketing according to the scale of each farm. When needed, Heather and Rachel will occasionally send products to sell on the Sea Bluff Farm stand.
“Twenty-two years into our business partnership, we certainly trust each other’s intentions,” Heather says. “Obviously, we disagree sometimes, and we may question each other’s decisions—but the one thing we never do is question each other’s intention behind the decision.” The foundation of Saanich Organics is friendship, and the clarity of trust and relationship is the spring that has fed the business over two decades.
Support & Mentorship
In the early years, Heather found support from the organic community, her husband, family, and business partners. She got involved with Islands Organic Producers’ Association (IOPA), and as she moved through the certification process, she found support in the organic standards.
“When I started farming, the certification system gave me a framework to learn about what organic production was, and to learn what best practices were,” says Heather. “The framework of the standards was my first primer on how to make choices to manage fertility and soil health.”
Going through the certification process and getting involved with IOPA brought other benefits as well. “The community that this all brought to me was important. I went to an IOPA AGM before I had even planted my first seed, and the people that I met on that first day became my first friends and mentors in the community.”
Heather acknowledges the local organic farming mentors who nurtured her along, including Rebecca Jehn (Rebecca’s Garden), Tina Baynes (Corner Farm), Mary Alice Johnson (ALM Farm), and Dieter Eisenhawer (Eisenhawer Organic Produce). Along with these mentors, Heather acknowledges her business partners Robin and Rachel as major pillars of support.
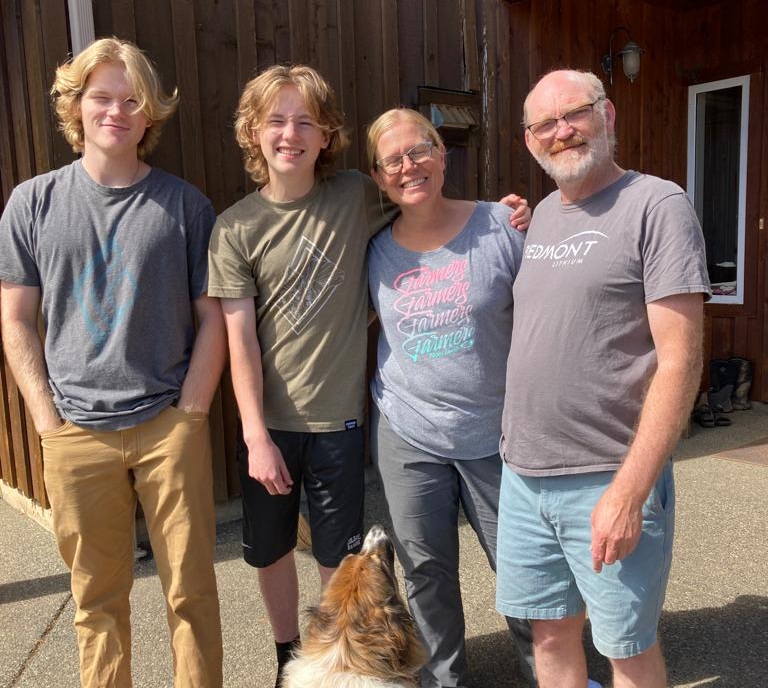

Financial Realities
For the first three years at Northbrook Farm, Heather managed the farm on her own, with help from Lamont. After that, they began to invite farm
apprentices in, and this morphed into paid farm hands, managed by Heather.
“In 2021, I decided to hire a field manager, because I didn’t want to feel guilty every moment that I wasn’t on the farm,” says Heather,
She’s been enjoying the challenge of learning how to effectively mentor farm managers. The most difficult part is making sure the managers have all the information they need to be successful, but at the same time, giving them some space to experiment. Heather says she’s trying to strike a balance “where I’m neither micromanaging, nor abandoning the farm manager.”
This is easier said than done due to the incredible financial pressure on the farm, Heather says. “The financial margins on a farm are so non-existent that there really is no room to say, oh, we’ll just let them figure it out and experiment.” With the increasing overhead of wages, supplies, and inputs, Heather walks this tightrope with grace, and respect for her employees.
Due to the rising costs of running a business, Heather says, “the sad reality is that the financial aspect of the farm is no less challenging than it was in year four or five. The farm makes way more money than it did in year five, but I don’t.” In short, the farm has made a huge increase in gross sales, but has not increased in profitability.
She clarifies that it’s her spouse Lamont’s off-farm income that allows the family to have the lifestyle that they enjoy. That being said, she continues, “the farm is my business, my career, and my job. And my career is not as financially lucrative as my spouse’s.”
“I don’t want anyone who comes to this farm to think, ‘Oh my gosh this is so awesome, you can have a farm and raise three kids, one’s away at school, one plays competitive sports, that this is all happening on a farming income.’” Heather quips, “I do not pay to raise my own children.”

Raising Kids and Vegetables
After her first year of farming, Heather was pregnant, and she received a crash course in farming full-time with a child. Five years later, Heather was farming full-time with three tots in tow.
She remembers one day when the kids were little, and it was a really bad year for mummy berry— Heather has a big blueberry patch. “I was walking by the greenhouse that Saanich Organics employee Mel Sylvestre was handling, and Mel hollered, ‘Hey Heather, the blight has just started in the tomatoes,’” Heather laughs.
“The kid was screaming, and I was exhausted,” she continues, “and I remember being so disheartened, and thinking, what am I doing?”
She thought about it for a moment, and realized, “I couldn’t think of anything else I would do. And that was almost the worst part, feeling like, ‘I’m in this too deep.’ And I didn’t have any reserves left in my body, mind, or spirit to step back and think, maybe I should not be farming right now.”
A few years later, someone Heather knew who was farming and pregnant said she wouldn’t be growing in the coming season, and that she would put everything into cover crops and take a maternity leave. Heather says, “my kids were elementary school age by that time, and my jaw dropped. It never actually occurred to me that I could take a break!” Her first baby was born in early January, and in early February she was starting seedlings. “I was doing crop planning right after I got home from the hospital with my baby,” she remembers.

Memorable Moments and People
Heather says the most joyous memories she has are “visual snippets.” Some of her best memories are “walking down to feed the chickens in the morning and seeing the early sunlight sparkling through the dew on the kale leaves.”
Her biggest treasure is “the composite joy and the sense of richness that I get when I step back and think of all the people who have come through the farm.”
“It’s not just because I got to work with Jay Williamson of Tendergreens Farm, and Josh who now runs Fat Chance Farmstead in Kingston, and Mel Sylvestre who now runs Grounded Acres on the Sunshine Coast,” she says. The network of farmers she has worked with over the years, “like Crystal and Ilya of Square Root Farm, and Rebecca Jehn, and first and foremost Robin and Rachel,” have brought a sense of richness to Heather’s life.
Similarly, Heather has played an important role in mentoring many farmers and apprentices: “Having the brilliance of these young people come through my life every year is a huge gift.” She says, “the apprentices and farm hands who have come through, whom I’ve gotten to spend a season or two with in what is often a very formative period in their lives—that’s where the really deep satisfaction comes in.”
Heather says that when her children were young, the farm hands and apprentices were a positive influence. “They were able to learn from, and respect many different people. That’s one thing I am really proud of at Northbrook Farm, is how many LGBTQ folks have worked here.” Heather continues, “that’s been a huge benefit to me and my family, because my kids have never been without the knowledge that being LGBTQ is a perfectly normal way to be in the world.”
Northbrook Farm and Saanich Organics are known throughout the local 2SLGBTQIA+ community for their support—they even sponsored the Rainbow Chard Queer Farmers Collective in the Victoria Pride Parade. It all started with a few employees early on having a great experience, and sharing that with others in their circles through word of mouth.
Organic Isn’t Just a Word
Besides her passion for environmental sustainability and community, the marketing advantage of certification appealed to Heather. “Even before we had mandatory organic, if you’re going to use a word as important as ‘organic,’ all legal requirements aside, it begs the question, what do you mean by that?”
“The definition of organic cannot be a simple one, and that’s how the standards have evolved, to define this term, organic,” says Heather. “Without that definition, the word is meaningless. Whenever we separate the word ‘organic’ from the [practice of the standards], it harms all of us. Organic is an agreement that we make among ourselves.”
Knowledge and practice of the organic standards requires lifelong study, expertise, and experience that is hard to convey to customers in a short conversation. “I don’t have time to have a conversation with every customer about exactly what all my soil fertility practices are, and what crop rotations look like on my farm,” emphasizes Heather. “More importantly, our customers should not have to be experts in agriculture to feel like they can eat good food, and make healthy and environmentally responsible choices.”
Heather points out the common misconception that “knowing your farmer” can replace the need for organic standards. “To say that a conversation between farmer and consumer replaces the need for organic certification is completely wrong,” she says. “Just because a person knows me, or because I’m nice, doesn’t mean I’m employing best practices. It does not guarantee that I am not using pesticides or chemical fertilizers.” Organic certification takes the guess-work out of relationships between farmers and consumers.
Pillars of Support
Heather Stretch has contributed a lot to the organic community in BC over the years. “I farm because I’m passionate about the food system,” she says. “In the beginning, it just felt like it was incumbent on me and everyone else who cares to step up. The longer you’re involved, the more you realize [the work is] important and interesting. And farmers are fun people to work with. Organic BC has given me the gift of community all around the province.”
“My pillar of support is the organic community in BC,” says Heather, “and the organic community needs the pillar of support that is Eva-Lena Lang. Eva-Lena is the unsung hero of the movement— she keeps this ship afloat through really turbulent waters.”
“There are also the wise, indefatigable women who somehow manage to spread joy at the same time as they spread wisdom,” says Heather, “like
Rebecca Kneen of Crannog Ales, and Anne Macey. They show up decade after decade, doing difficult and often boring work—but they bring joy when they do it.”
“And now the younger men like Jordan Marr and Tristan Banwell,” she continues, “and Tristan’s wife Aubyn needs a shout-out—she’s the reason that Tristan can do this work. All of our pillars of support have support underground that we may or may not see.” This underground support is so important to the success of farmers, whether in the field, or in community work.
The Future of Northbrook Farm
“Over the years, my role is changing,” Heather says, “I don’t do much seeding, weeding, thinning, or harvesting anymore. I do the business planning, the marketing, the bookkeeping, the purchasing, and everything that needs to happen on weekends, like watering.”
When asked what she’s excited about for the future for her farm, Heather talks about her commitment to increasing profitability to achieve her goals of higher wages for employees, and to retain workers for many seasons to come. Heather wants her farm manager role to be an employment opportunity that lasts more than a year or two—she’s hoping to “provide career track employment for farmers, rather than just seasonal work.”
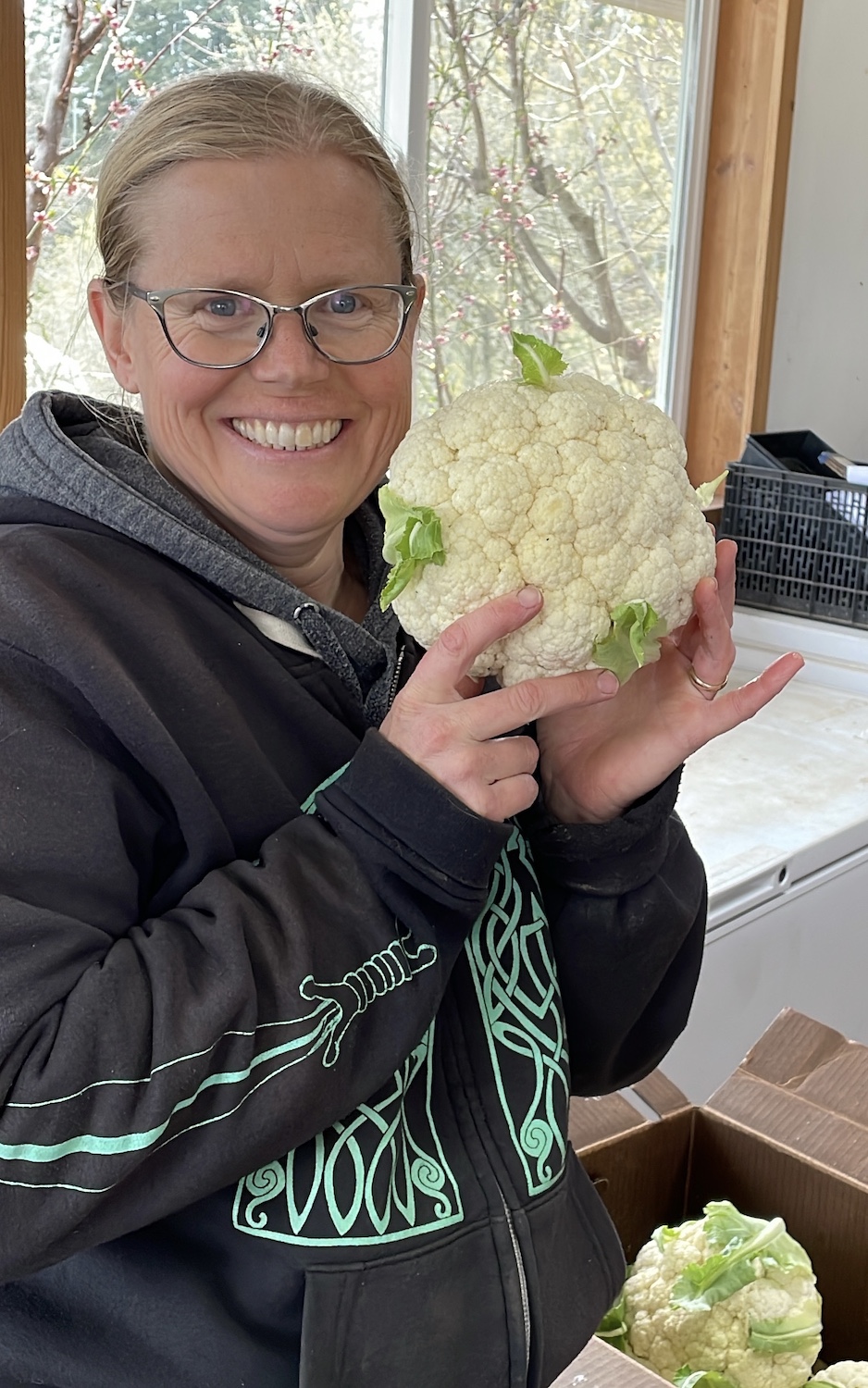
Meanwhile, in the field, Heather is excited about her overwintered cauliflower, “because it’s such a rare and wonderful thing when it actually works!” She gushes, “the way the cauliflower heads just pop out of the leaves—one day there are these plants with no white showing and the next day you go down to look, and there are beautiful cauliflower heads!”
Heather is always up for an experiment, “This year I’m trying a crop of main season cauliflower, which I’ve never succeeded in. Hope springs eternal!”
Hope truly does spring eternal in the fields at Northbrook Farm, where community and collaboration have created a rich tapestry of people and food that will benefit generations to come.
Moss Dance is the layout designer for the BC Organic Grower, a once-and-future vegetable farmer with a big garden, and a newly practicing acupuncturist on the territories of the Hul’qumi’num and SENCOTEN speaking peoples on Salt Spring Island.
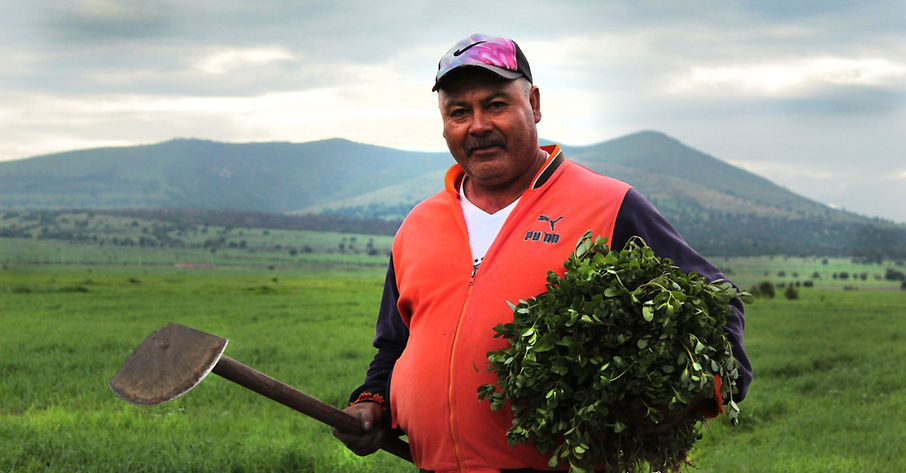
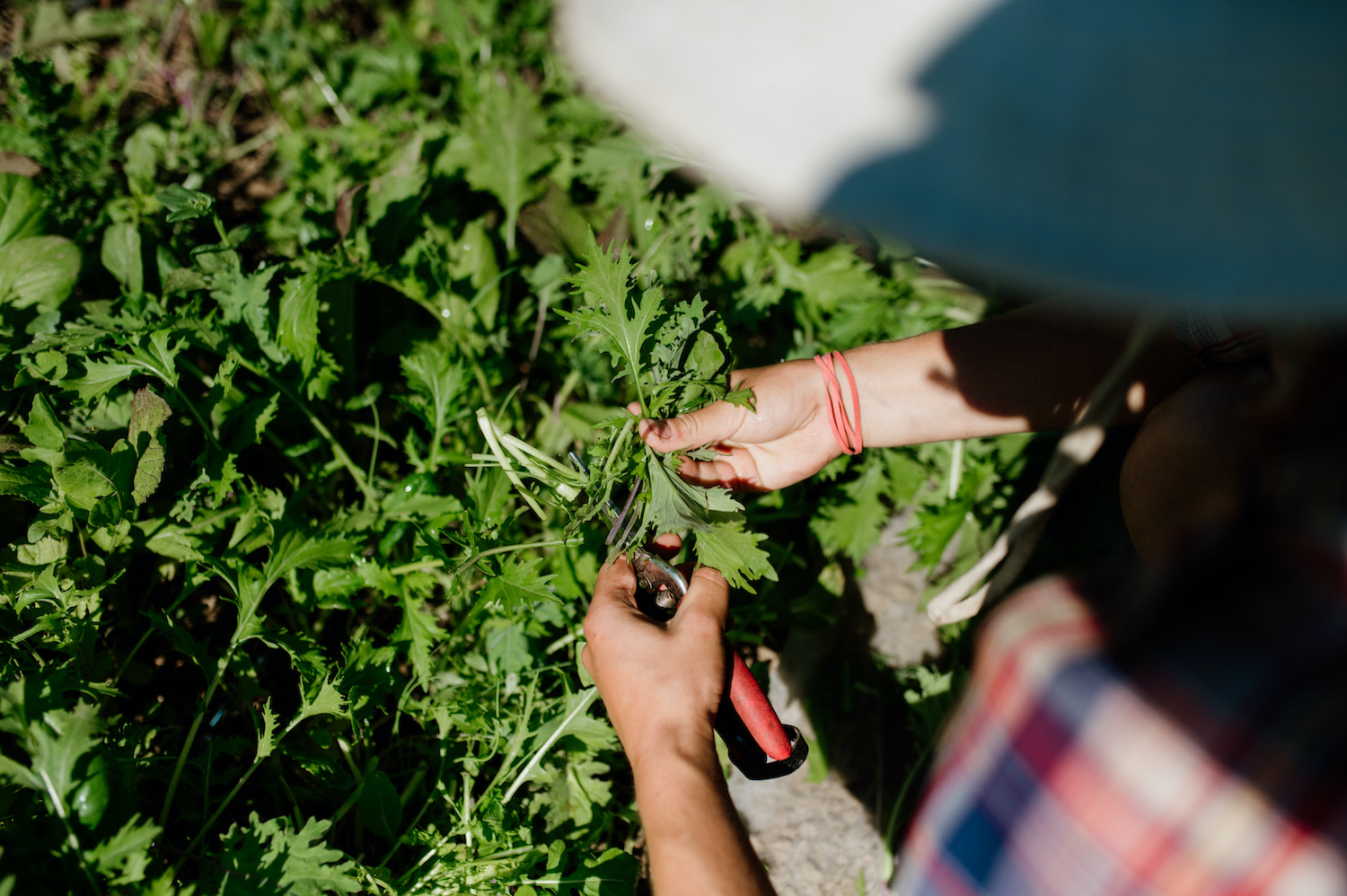
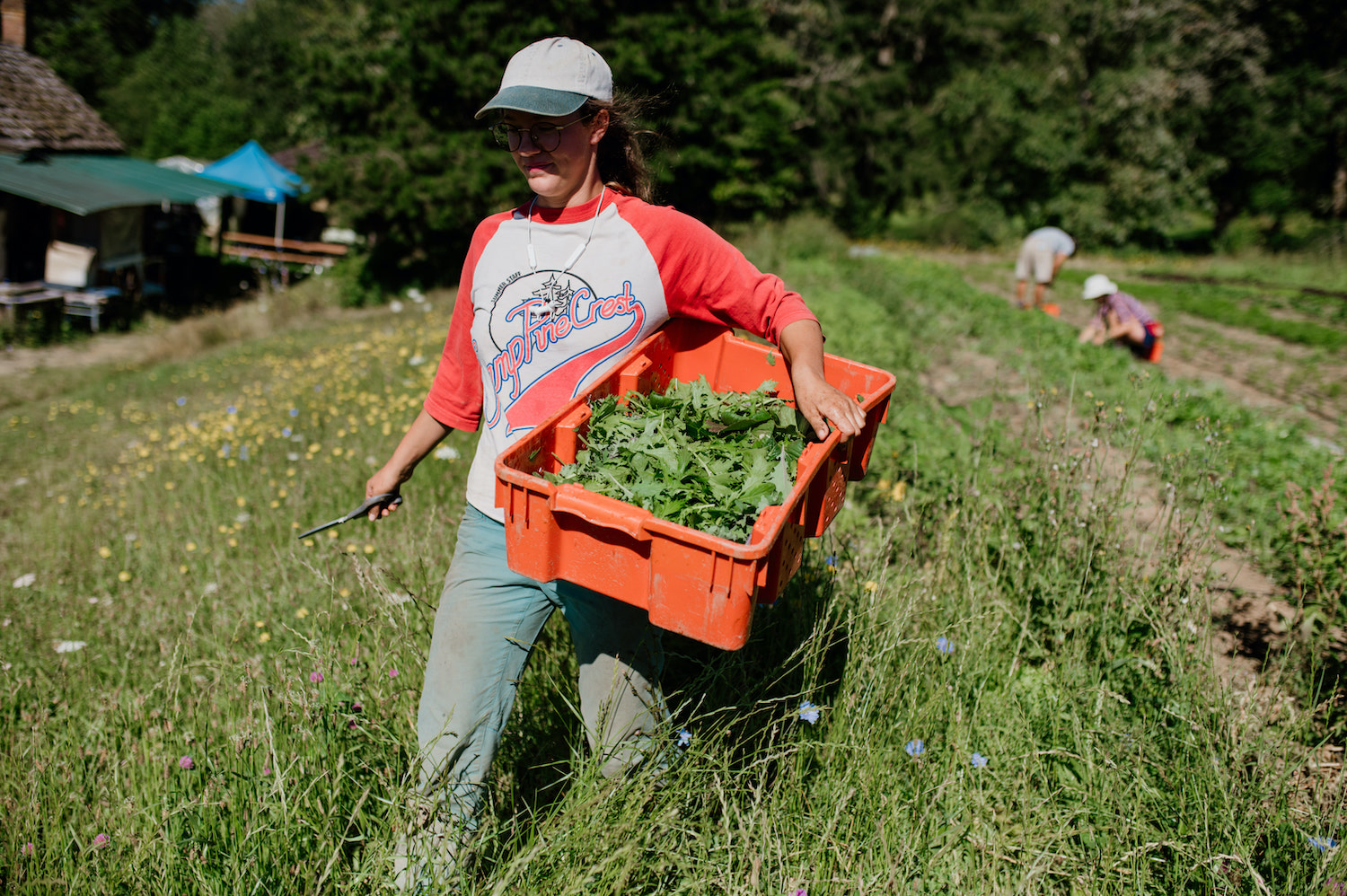
Featured image: Salad green harvest at Northbrook Farm. Credit: Maylies Lang.